- Facebook280
- Twitter1
- Total 281
A recent paper entitled “A Complex Systems Approach to the Study of Ideology”* presents a theory much like the one I have begun to develop in a series of posts on this blog and other work.
The authors write,
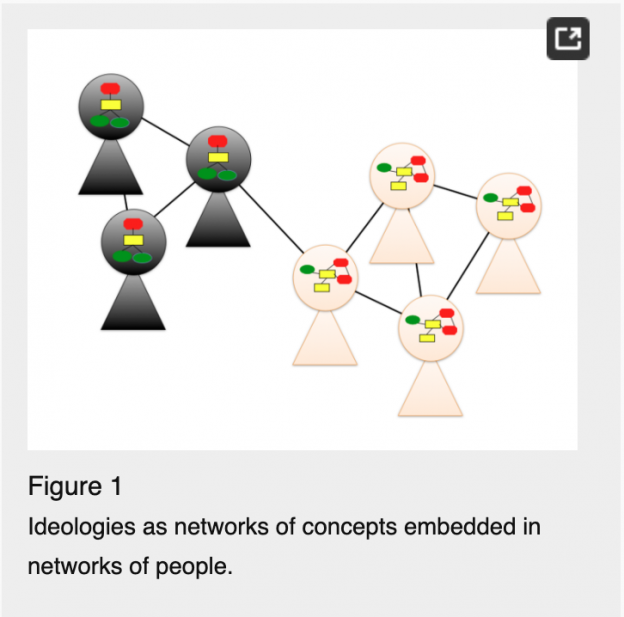
If we construe ideologies as complex systems, we have (at least) two levels of systems embedded in each other. At the individual level, the elements are ideas, beliefs, and values, whose interactions give rise to a person’s understanding of society, which in turn guides individual political behavior. At the group level, the elements are individual minds whose interactions give rise to discourses and power dynamics, which in turn guide collective action and societal change. We thus conceive of an ideological system as a network of minds, where minds are networks of concepts.
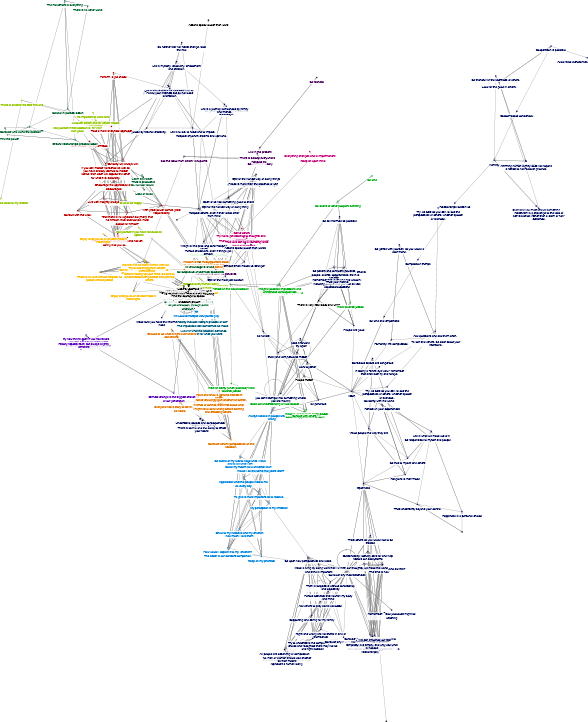
Fig 1 illustrates their model. Compare a diagram of the ideas held by my undergraduate class some years ago (with each student’s ideas in a different color):
The authors of “A Complex Systems Approach” also diagram the ideology of the Tea Party Movement, using the qualitative analysis in a well-known article by Vanessa Williamson, Theda Skocpol, and John Coggin as their material.
Their diagram of the Tea Party is not heavily documented, but it demonstrates a payoff of their method. A paradox about the Tea Party is that they were powerful opponents of Obamacare yet passionate defenders of Medicare. The authors of “A Complex Systems Approach” explain this pattern by arguing that “representations of social programs are connected on one hand with representations of the self as a hard worker contributing to society and, hence, deserving of the government check …, but on other hand with the highly negative representations of government, spending, and taxation common to conservative ideologies.”
Each idea and link in the Tea Party ideology is consistent enough in its own way, and the overall system generates a combination of policy positions that only seem inconsistent if you try to place the whole ideology on one linear spectrum from pro- to anti-welfare. As a network of ideas, the ideology is as well structured as many others are. This is not an endorsement, since some of the specific nodes in the Tea Party’s network are objectionable by my lights. But a complex systems model offers a more refined analysis.
The word “complex” is used loosely and in various ways, but the authors of “A Complex Systems Approach” mean systems that exhibit “emergence, nonlinearity (disproportionality of cause and effect), path dependency, and multiple equilibria.” In the Tea Party ideology, for example, resentment of groups perceived as undeserving (which, in turn, is a racialized perception) has a powerful effect because of its location in the whole network. The Tea Party can land in several places (libertarian or #MAGA) that reflect multiple equilibria.
I find it intuitive that our ideas are structured and that the structures matter apart from the lists of individual ideas we hold. I acknowledge that we are not necessarily conscious of the whole structures of our own thought. Self-consciousness requires critical introspection and/or interaction with other people, and it is always partial.
However, I do believe we are conscious of portions of the network at any given time–not just the individual ideas, but the connections among them. Much of our discourse is about mini-structures of ideas, e.g., “I think this because of that.” Methods that reveal structures of ideas and links are alternatives to the family of methodologies that use latent variables to “explain” lists of specific beliefs, as in Moral Foundations Theory. I believe that such methods assume rather than demonstrate that human beings are driven by a few unconscious psychological traits. Although such explanations offer some insight, they should be combined with methods that allow us to see how people and groups build more complex structures. This is why I am excited to see this new paper and the work that underlies it.
* Homer-Dixon, Thomas, Jonathan Leader Maynard, Matto Mildenberger, Manjana Milkoreit, Steven J. Mock, Stephen Quilley, Tobias Schröder, & Paul Thagard. “A Complex Systems Approach to the Study of Ideology: Cognitive-Affective Structures and the Dynamics of Belief Systems.” Journal of Social and Political Psychology [Online], 1.1 (2013): 337-363. Web. 4 May. 2020. I had been previously influenced by Thagard’s work although I have not made the detailed study of it that it deserves.
See also: judgment in a world of power and institutions: outline of a view; from I to we: an outline of a theory; an alternative to Moral Foundations Theory; etc. `